
Hemorrhoids affect millions worldwide and can cause discomfort, bleeding, and pain. In this guide, we’ll explore what hemorrhoids are, what causes them, how they are diagnosed and treated, and what the latest research tells us—all in a clear, humanized manner.
1. What Are Hemorrhoids?
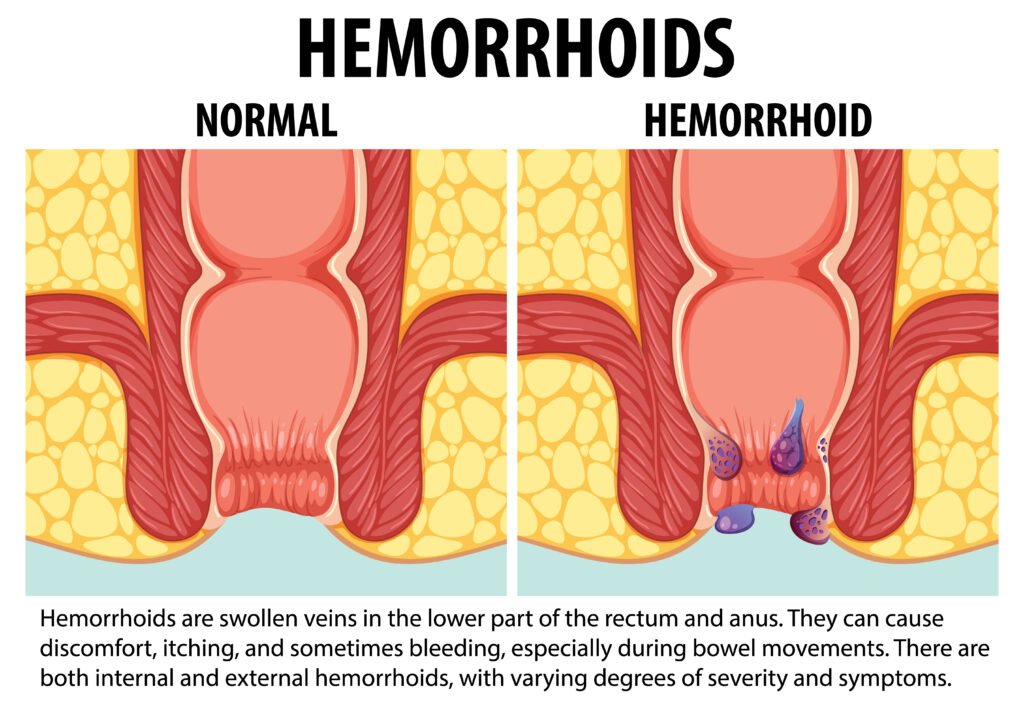
You could say that hemorrhoids are rectal cushions that become swollen. They come in two main types.
•Internal Hemorrhoids: Located inside the rectum, these are often painless but may cause bleeding.
•External Hemorrhoids: Found under the skin around the anus, they can cause pain, itching, and swelling. This condition often occurs meaning it happens to many of us. Though it is uncomfortable, it is rarely dangerous. As Harvard Health states symptoms of hemorrhoids show 50 percent of the population suffers from them by age 501.
2. What Causes Hemorrhoids?
Many things can cause hemorrhoids to form, including.
• Straining during bowel movements: Often due to chronic constipation or hard stools.
• Prolonged sitting: Especially on the toilet, which increases pressure in the anal region.
• Pregnancy: The growing uterus puts pressure on pelvic veins.
• Low-fiber diet: This can lead to constipation and increased.
Studies have shown that lifestyle and dietary habits play a major role in hemorrhoid formation 1. Recent research also indicates that higher resting anal canal tone may contribute to the condition 2.
3. What Are the Common Symptoms of Hemorrhoids?
People with hemorrhoids might experience.
• Bleeding: Bright red blood on toilet paper or in the bowl.
• Pain and discomfort: Especially with external hemorrhoids or when a blood clot (thrombosis) forms.
• Itching and irritation: Due to mucus discharge or inflammation.
• Prolapse: Internal hemorrhoids may protrude outside the anus.
These symptoms can be mild to severe. While they can be uncomfortable, they typically get better with treatment. 1.
4. How Are Hemorrhoids Diagnosed?
Usually simple, the diagnosis consists of the following steps:
• Physical Examination: A physician examines the anal region and may do a digital rectal exam.
• Anoscopy or Proctoscopy: The doctor can see internal hemorrhoids using tiny scopes.
• Extra Procedures: To rule out other reasons in situations of severe bleeding, sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy may be advised. This easy diagnostic method makes sure hemorrhoids are properly recognized and treated. 1.
5. What Treatment Options Are Available for Hemorrhoids?
Treatment is based on the degree of symptoms:
• Conservative management:
• Increased fiber intake and hydration.
• Sitz baths and topical treatments.
• Over-the-counter pain medications.
• Office procedures:
• Rubber band ligation, in which an elastic band interrupts blood circulation.
• Chemical injection sclerotherapy to shrink the hemorrhoid • Laser therapy for minimally invasive pain relief and improved quality of life. 5
• Surgical options:
• Hemorrhoidectomy is performed for severe or recurring instances.
• Stapled hemorrhoidectomy for internal hemorrhoids with prolapse.
Recent studies comparing techniques—such as laser treatments vs rubber band ligation—have indicated lower postoperative discomfort and greater symptom resolution with newer technologies. 5
. Other research has evaluated combined techniques (like injection sclerotherapy with external hemorrhoidectomy) to minimize complications 2.
6. What Does the Latest Research Tell Us About Hemorrhoid Management?
Recent clinical studies and reviews have shed light on advanced treatments:
- Emerging Procedures: Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization with mucopexy has been demonstrated to have similar long-term outcomes to conventional surgery but with higher short & improved quality-of-life 4.
- Combination Therapies: New techniques that combine injection sclerotherapy with minor surgical procedures are being explored to reduce postoperative complications while maintaining efficacy 2.
- Comparative Studies: Reviews of treatments—including rubber band ligation and laser procedures—indicate that while each method has its merits, patient comfort and long-term outcomes are key considerations 3.
These findings emphasize a trend toward minimally invasive techniques that offer effective symptom relief with fewer complications.
7. How Can Hemorrhoids Be Prevented?
Prevention: Focuses on lifestyle & diet changes
•Increase Fiber Intake: Consume fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to move the stool without straining.
•Stay well hydrated as some constipation can be prevented by drinking enough water.
• Exercise regularly: Physical exercise helps with good digestion.
• Do not strain: go to the washroom and push when you feel like going for a bowel movement instead of spending long hours trying to force your body.
• Manage a healthy weight: Decreases pressure on pelvic veins
Research has shown that even simple changes can significantly reduce the risk of hemorrhoids 6.
8. What Is the Future Outlook for Hemorrhoid Treatment?
New therapies enhance management:
• Devices / Minimally Invasive — Expect laser dearterialization and dearterialization with mucopexy to be used more commonly.
• Better Clinical outcomes: Further studies aim to hone times of recovery and recurrences
• Personalized Pharma: Studies in the future may offer more targeted strategies depending on individual risk factors and symptom profiles.
Quality of life gets better with the help of new and minimally invasive approaches to treat the discomfort.
Conclusion
Patients When it comes to managing the pain from Hemorrhoids -causes, symptoms of diagnosis, and treatment, one tends not to allow the condition to turn into serious complications of any sort. With treatments improving so very quickly due to new research, patient comfort and speed of return to the fields. In case If the thought of figuring out sounds misleading, ask your healthcare provider for an appropriate strategy for your condition.
References
- Harvard Health Publishing. Hemorrhoids: A to Z. https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/hemorrhoids-a-to-z
- PubMed. Efficacy and Safety of a New Technique Combining Injection Sclerotherapy and External Hemorrhoidectomy for Prolapsed Hemorrhoids. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39473713/
- PubMed. Hemorrhoid Disease: A Review on Treatment, Clinical Research and Patent Data. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37106517/
- PubMed. Transanal Hemorrhoidal Dearterialization With Mucopexy Versus Ferguson Hemorrhoidectomy for Prolapsed Internal Hemorrhoids: A Multicenter Prospective Study. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37325897/
- PubMed. The Hemorrhoid Laser Procedure Technique vs Rubber Band Ligation: A Randomized Trial Comparing 2 Mini-invasive Treatments for Second- and Third-degree Hemorrhoids. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21552053/
- MedlinePlus. Hemorrhoids. https://medlineplus.gov/hemorrhoids.html